Heat of reaction for, CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)at constant V is 67.71 K cal at 17^° C. The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^° C is
Heat of reaction for, CO(g) + 1/2 O2(g)→ CO2(g)at constant V is 67.71 K cal at 17^° C. The heat of reaction at constant P at 17^° C is
Heat of reaction for- CO-g- - 1-2 O2-g- CO2-g-at constant V is-67-71 K cal at 17- C- The heat of reaction at constant P at 17- C is

A 2.200-g sample of quino ne $$ (C_6H_4O_2) $$ is burned

The heat of formation of CO(g) and CO2(g) are ΔH=−110 and ΔH=−393kJmmol−1 respectively. What is the heat of reaction(ΔH) (in kJ mol−1) the following reaction?CO(g)+12O2(g)→CO2(g)
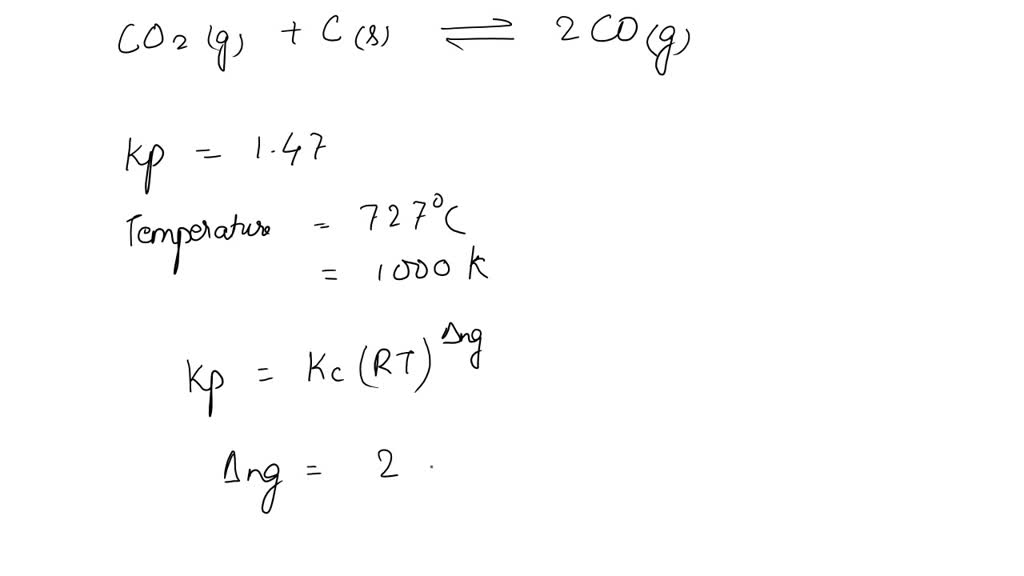
SOLVED: Kp for the reaction CO2(g) + C(s) ⇌ 2CO(g) is 1.47 at 727°C. Calculate Kc at this temperature.

Thermodynamics & Thermochemistry - Master Assignment - NEET
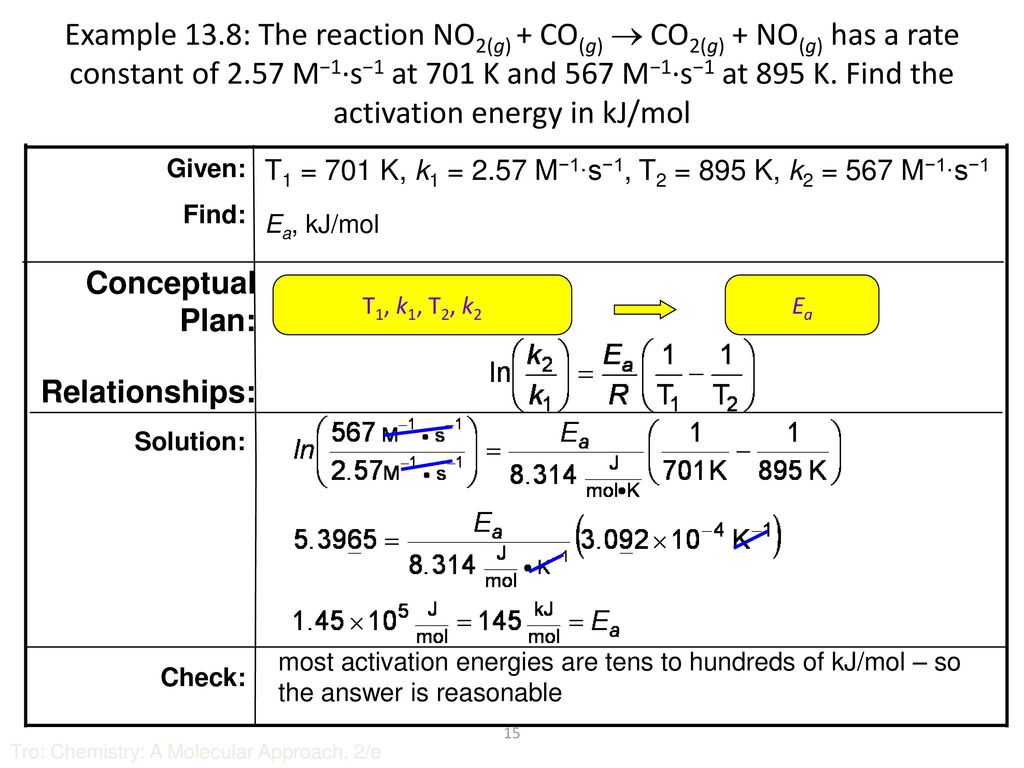
Chapter 13: Chemical Kinetics - ppt download

heat evolved in the reaction H2 + cl2 gives to HCL is 182 kj/mole bond energy of H2,cl2 are 430 and

Solved Question 27 (1 point) In the reaction, CO (g) + NO2
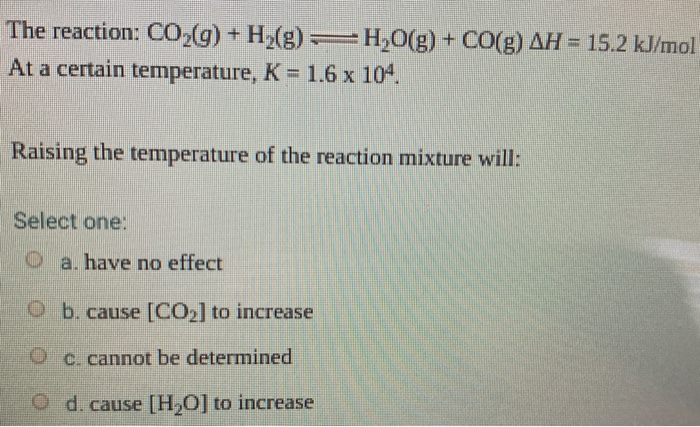
Solved The reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) = H2O(g) + CO(g) AH =

For CaCO3( s)→CaO(s)+CO2( g) at 977∘C, ΔH=174 kJ/mol; then ΔE is :-..
Essential Pharma Documents: February 2017

Activation of C−H Bonds by Metal Complexes
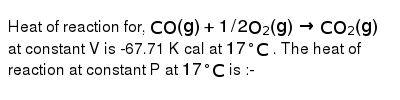
Heat of reaction for, CO(g)+1//2O(2)(g)rarr CO(2)(g) at constant V is

Heat of reaction CO(g) + 1/20,(g) → CO. (g) constant V is -67.71 Kcal 17°C. The heat of reaction constant Pat 17°C is :- (1) -68.0 Kcal (2) + 68.0 Kcal (3) -67.42 Kcal (4) None

Solved Question 27 (1 point) In the reaction, CO (g) + NO2









