Sensors, Free Full-Text
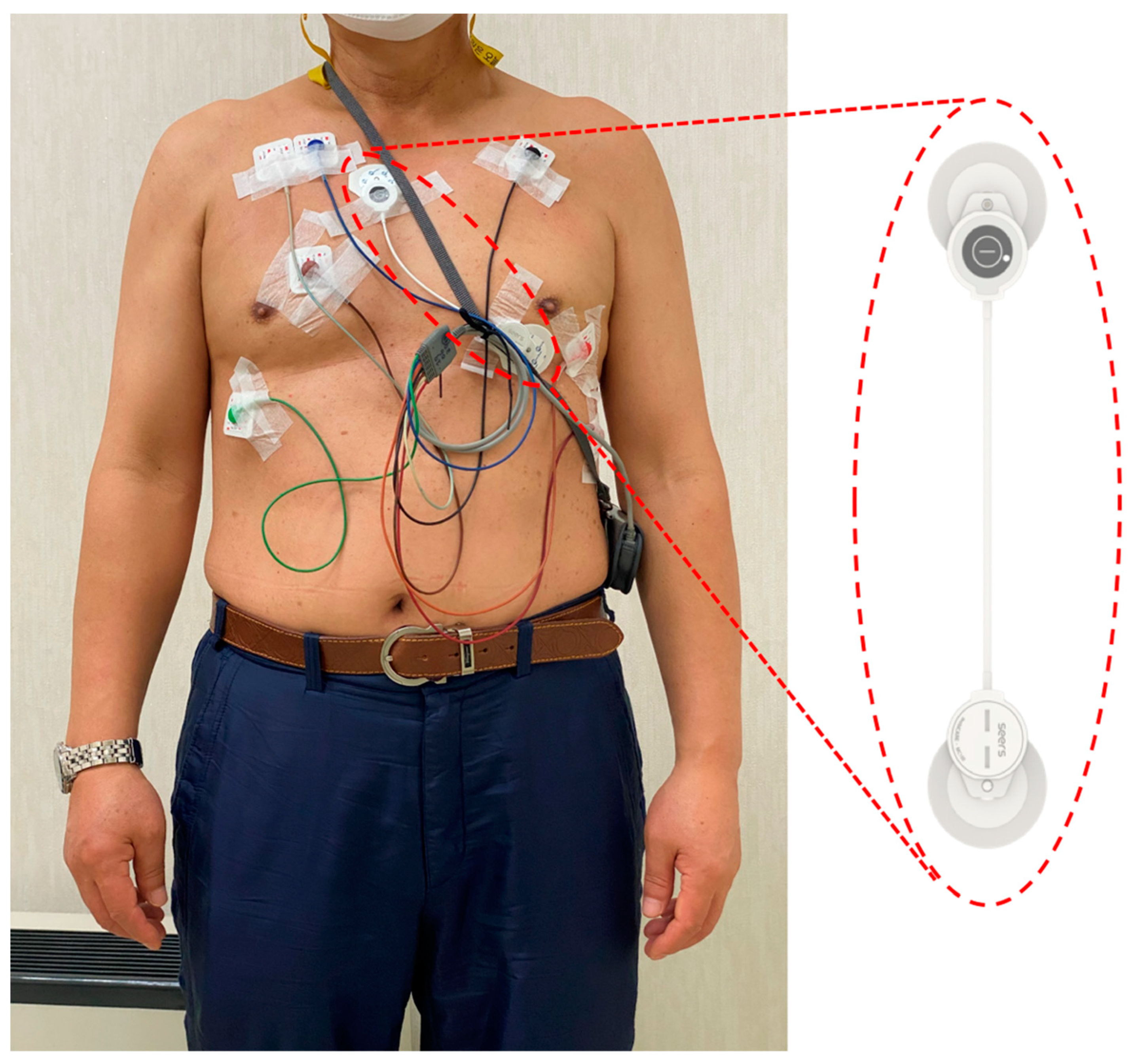
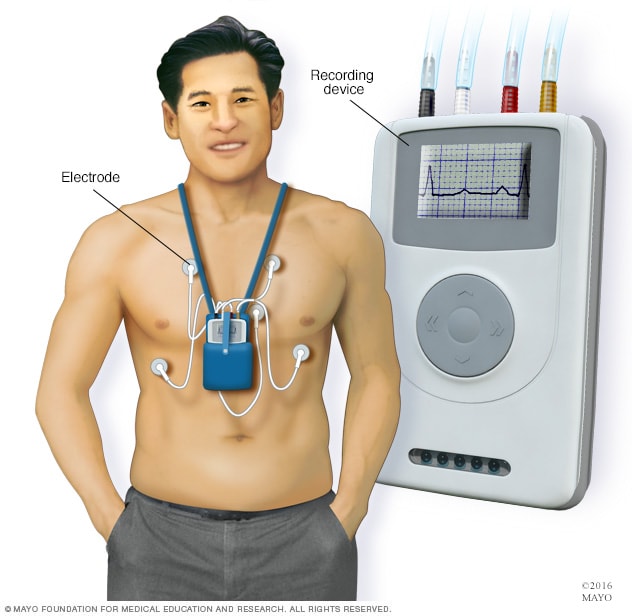
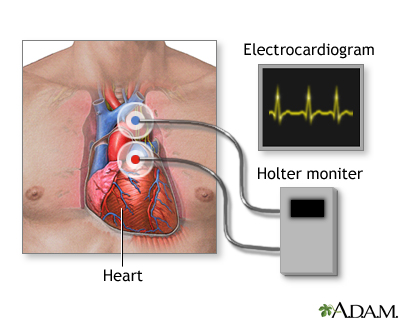
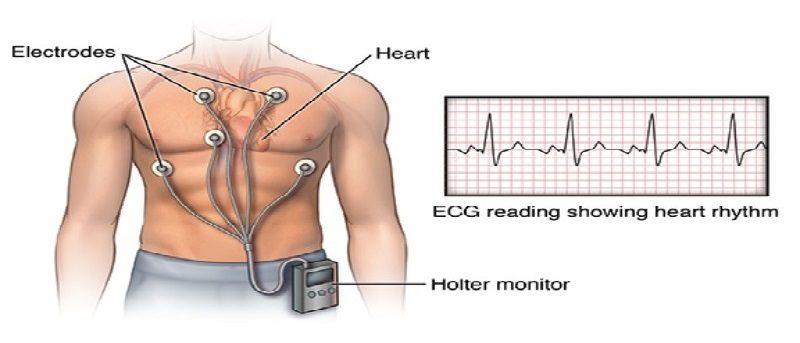
There are few reports on head-to-head comparisons of electrocardiogram (ECG) monitoring between adhesive single-lead and Holter devices for arrhythmias other than atrial fibrillation (AF). This study aimed to compare 24 h ECG monitoring between the two devices in patients with general arrhythmia. Twenty-nine non-AF patients with a workup of pre-diagnosed arrhythmias or suspicious arrhythmic episodes were evaluated. Each participant wore both devices simultaneously, and the cardiac rhythm was monitored for 24 h. Selective ECG parameters were compared between the two devices. Two cardiologists independently compared the diagnoses of each device. The two most frequent monitoring indications were workup of premature atrial contractions (41.4%) and suspicious arrhythmia-related symptoms (37.9%). The single-lead device had a higher noise burden than the Holter device (0.04 ± 0.05% vs. 0.01 ± 0.01%, p = 0.024). The number of total QRS complexes, ventricular ectopic beats, and supraventricular ectopic beats showed an excellent degree of agreement between the two devices (intraclass correlation coefficients = 0.991, 1.000, and 0.987, respectively). In addition, the minimum/average/maximum heart rates showed an excellent degree of agreement. The two cardiologists made coherent diagnoses for all 29 participants using both monitoring methods. In conclusion, the single-lead adhesive device could be an acceptable alternative for ambulatory ECG monitoring in patients with general arrhythmia.
Sensors, Free Full-Text, thomas mitchell overton execution

Sensors & Diagnostics journal

Free Sensors eBooks

TEKSCAN Pressure Mapping / Force Measurement / Tactile Sensor 3000/P1/1429T1/REG
Free Dwg Viewer 6.2 Rad Portable - Colaboratory
Sensors, Free Full-Text
Sensors, Free Full-Text
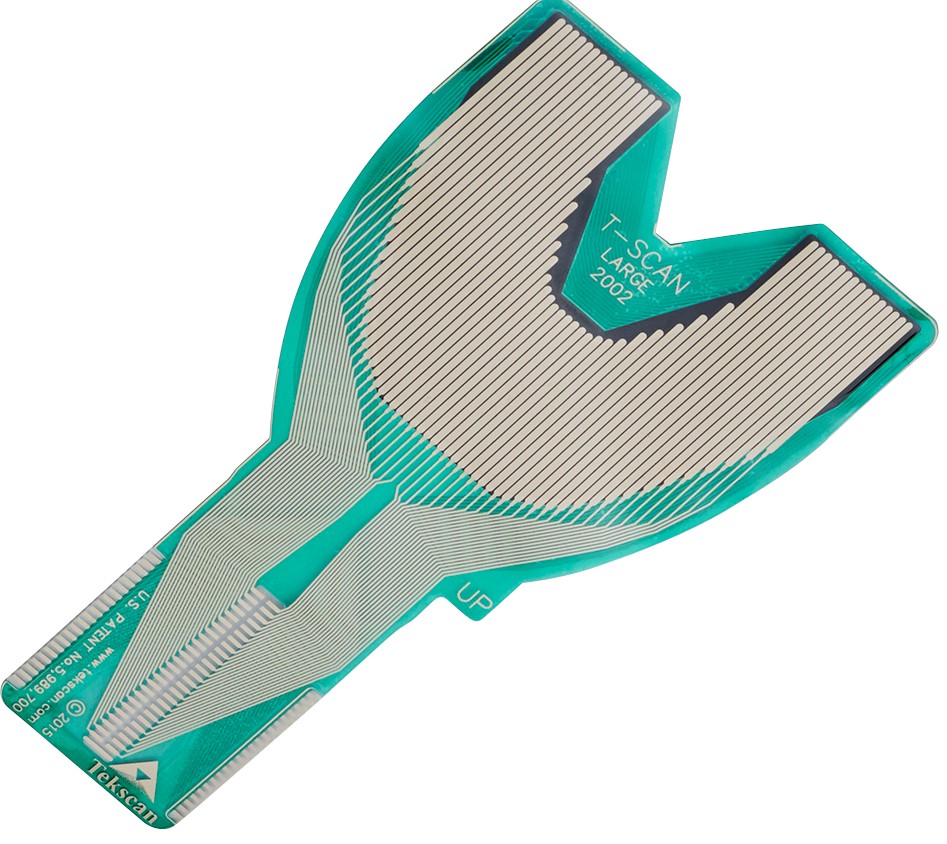

Sensors for Pressure Mapping and Force Measurement

Battery-free, wireless soft sensors for continuous multi-site measurements of pressure and temperature from patients at risk for pressure injuries